You are here
Architecture
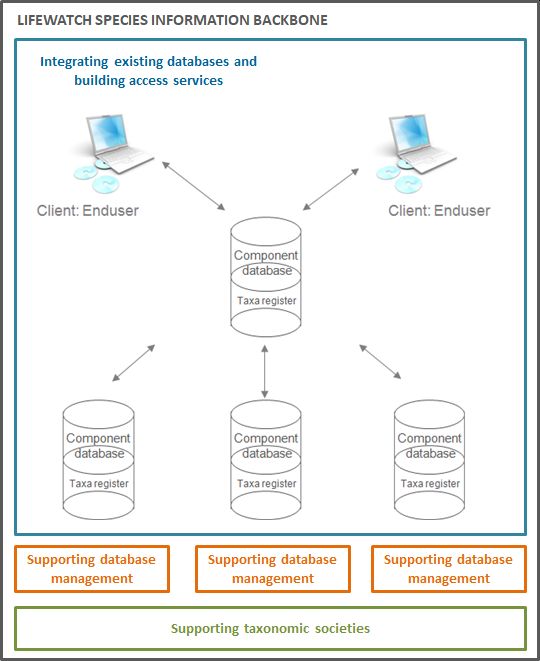
The LifeWatch Species Information Backbone (LW-SIBb) standardises species data and integrates biodiversity data from different repositories and operating facilities and is the driving force behind the species information services of the Belgian LifeWatch.be e-Lab.
Species Information Backbone
Because of its internationally recognized expertise in building taxonomic databases and related web services, the Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) was selected to set up the LifeWatch Species Information Backbone (LW-SIBb) as a central part of the European LifeWatch infrastructure. The aim of the LW-SIBb is to (virtually) bring together different component databases and data systems, all of them related to taxonomy, biogeography, ecology, genetics and literature.
The scheme below represents the currently identified data systems that deal with one or more of these components. Ideally, a data flow can be established between all these systems, ensuring that there is a strong and continuously supported flow of data and information from (and between) the national and regional levels to the thematic and global levels. Some systems are already strongly interlinked, while for others the data flow mechanisms and links still need to be established. During the further construction and maintenance phase, these links will be further explored and developed.

Coordination of the LW-SIBb is practiced at three parallel levels:
|
|
|