You are here
RV Simon Stevin sampling campaigns
The RV Simon Stevin is a multidisciplinary research vessel deployed for academic coastal and oceanographic research in the Southern Bight of the North Sea and the eastern part of the English Channel.
RV Simon Stevin
The research vessel meets the requirements of the various marine research disciplines in Flanders, and is equipped with all standard sampling equipment as well as sophisticated sonar technology for flow measurements and soil characterization. It is used mainly for daytime operations, but overnight trips may be planned as well. It also serves as a training platform for students from marine sciences as well as maritime training courses, and as a testing platform for new technologies. In addition, educational trips for primary and secondary schools are organized aboard the vessel. The ship sails under the Belgian flag and is registered in Ostend. More information about the technical specifications, management, operability, construction and funding can be found here. You can also follow the events aboard the research vessel on the RV Simon Stevin Facebook page.
MIDAS
When at sea, a data system aboard the RV Simon Stevin registers the navigation data as well as meteorological and oceanographic (physicochemical) data. Marine scientists log their research activities during each trip. The system also helps to plan cruises and to register ship activities. All data is kept and managed in the MIDAS database, which stands for Marine Information and Data Acquisition System. The real-time position of the Simon Stevin and the real-time activities aboard the research vessel are also displayed on the map of the LifeWatch Observatory, accessible through the homepage.
LifeWatch surveys
Since 2002, VLIZ has sampled 10 stations in the Belgian part of the North Sea on a monthly basis - prior to 2012 aboard the RV Zeeleeuw, from then onwards aboard the RV Simon Stevin. During these surveys, water and soil samples were taken and CTD measurements were performed. As part of the LifeWatch marine observatory, these surveys were redesigned. A grid of 9 LifeWatch stations is orientated along an east-west gradient and covers the coastal zone. These stations are sampled monthly during 1-day surveys (circles on the map below). Seasonally, 8 additional LifeWatch stations, located further at sea, are sampled during 2-day surveys according to an offshore-inshore gradient (squares on the map below).
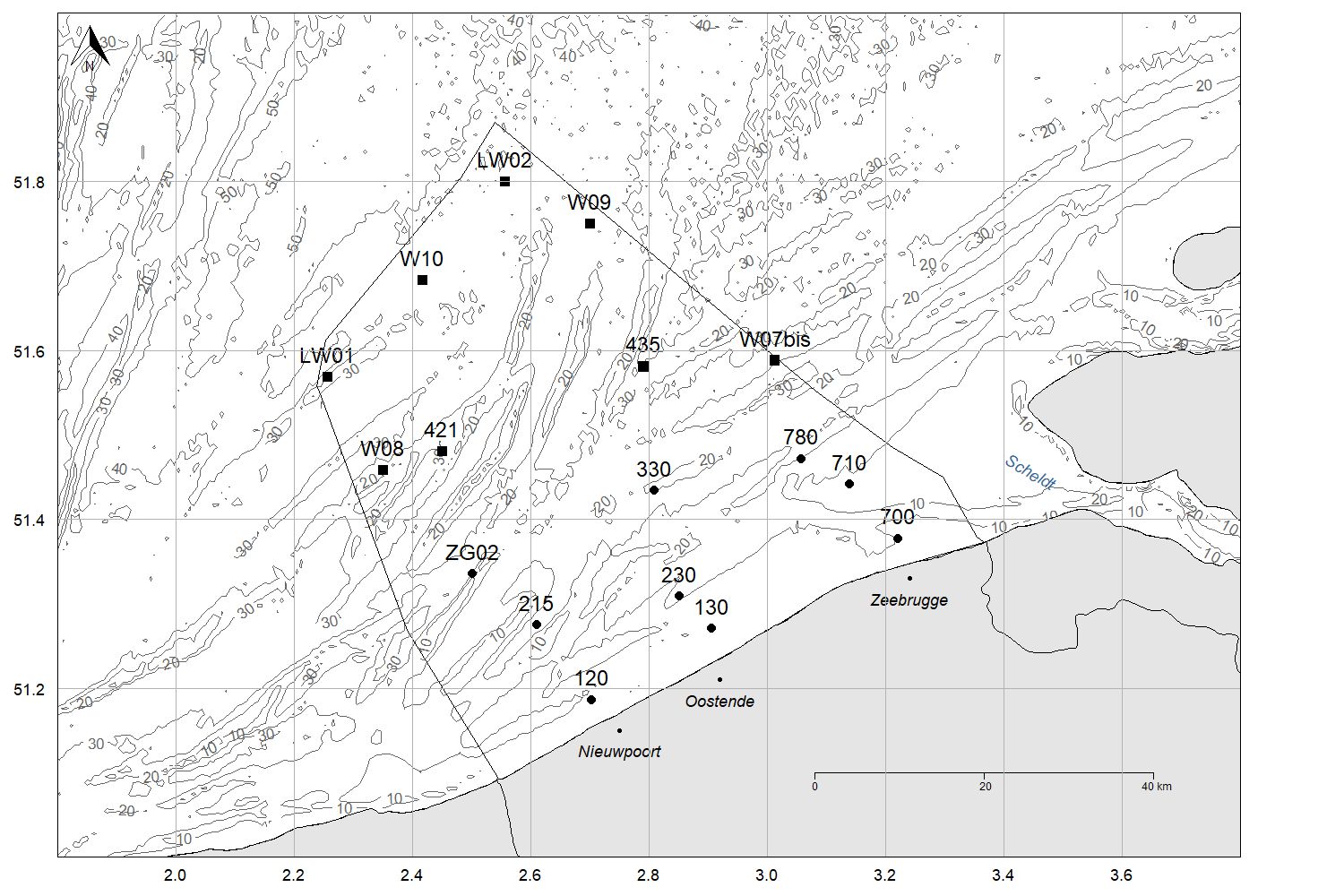
Map with LifeWatch stations sampled during monthly 1-day (circles) and seasonal 2-day (squares) sampling campaigns.
LifeWatch sample library
During these LifeWatch surveys, various seawater and seabed characteristics are measured: depth profile of the water column (temperature, salinity, turbidity, oxygen concentration, light scatter and acidity), water sample parameters (nitrate and phosphate concentration, chlorophyll-a and other pigments and suspended particulate matter), water transparancy (Secchi depth), and grain size of the bottom samples. The biological samples include zooplankton, macrobenthos and phytoplankton. An overview of the available samples can be found in the LifeWatch Sample Library.




Left to right (©VLIZ): Processing a macrobenthos sample - Zooplankton samples - Sampling the microbial biodiversity - Secchi disc
Data
Data can be accessed via the LifeWatch Data Explorer for underway data and the LifeWatch Data Explorer for station data.
Metadata is available at:
- LifeWatch observatory data: nutrient, pigment, suspended matter and secchi measurements in the Belgian Part of the North Sea, More
- MIDAS: Marine Information and Data Acquisition System: Underway & Cruise data, More
Useful links
- LifeWatch Data Explorer - Monitoring station data: Access and explore the LifeWatch data.
- LifeWatch Data Explorer - Underway data: Access and explore the LifeWatch data.
- Sample library: Visit the campaign sample library of the Belgian LifeWatch Observatory.
Selection of recent publications
- Mortelmans, J.; Aubert, A.; Reubens, J.; Otero, V.; Deneudt, K.; Mees, J. (2021). Copepods (Crustacea: Copepoda) in the Belgian part of the North Sea: Trends, dynamics and anomalies. J. Mar. Syst. 220: 103558. https://hdl.handle.net/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2021.103558 [link to IMIS record]
- Castagna, A.; Dierssen, H.; Organelli, E.; Bogorad, M.; Mortelmans, J.; Vyverman, W.; Sabbe, K. (2021). Optical detection of harmful algal blooms in the Belgian coastal zone: A cautionary tale of Chlorophyll c3. Front. Mar. Sci. 8: 770340. https://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.770340 [link to IMIS record]
- Hablützel, P.I.; Rombouts, I.; Dillen, N.; Lagaisse, R.; Mortelmans, J.; Ollevier, A.; Perneel, M.; Deneudt, K. (2021). Exploring New Technologies for Plankton Observations and Monitoring of Ocean Health, in: Kappel, E.S. et al. Frontiers in ocean observing: Documenting ecosystems, understanding environmental changes, forecasting hazards. Oceanography, Suppl. 34(4): pp. 20-25. https://dx.doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2021.supplement.02-09 [link to IMIS record]
- Royer, C.; Borges, A.V.; Martin, J.L.; Gypens, N. (2021). Drivers of the variability of dimethylsulfonioproprionate (DMSP) and dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) in the Southern North Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 216: 104360. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2021.104360 [link to IMIS record]
- Pint, S.; Everaert, G.; Theetaert, H.; Vandegehuchte, M.B.; Gkritzalis, T. (2020). Air–sea carbon flux from high-temporal-resolution data of in situ CO2 measurements in the southern North Sea. Biogeosci. Discuss. (preprint). https://dx.doi.org/10.5194/bg-2020-442 [link to IMIS record]
- Mortelmans, J.; Deneudt, K.; Cattrijsse, A.; Beauchard, O.; Daveloose, I.; Vyverman, W.; Vanaverbeke, J.; Timmermans, K.; Peene, J.; Roose, P.; Knockaert, M.; Chou, L.; Sanders, R.; Stinchcombe, M.; Kimpe, P.; Lammens, S.; Theetaert, H.; Gkritzalis, T.; Hernandez, F.; Mees, J. (2019). Nutrient, pigment, suspended matter and turbidity measurements in the Belgian part of the North Sea. Scientific Data 6(1): 22. https://hdl.handle.net/10.1038/s41597-019-0032-7 [link to IMIS record]
- Deschutter, Y.; De Schamphelaere, K.; Everaert, G.; Mensens, C.; De Troch, M. (2019). Seasonal and spatial fatty acid profiling of the calanoid copepods Temora longicornis and Acartia clausi linked to environmental stressors in the North Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 144: 92-101. https://hdl.handle.net/10.1016/j.marenvres.2018.12.008 [link to IMIS record]
